Health
Understanding Abscesses: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
Abscesses are a common yet often misunderstood medical condition. These painful, swollen masses filled with pus can occur anywhere in the body and can be quite distressing. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of abscesses, exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatment options to help you better understand this medical issue.
What Is an Abscess?
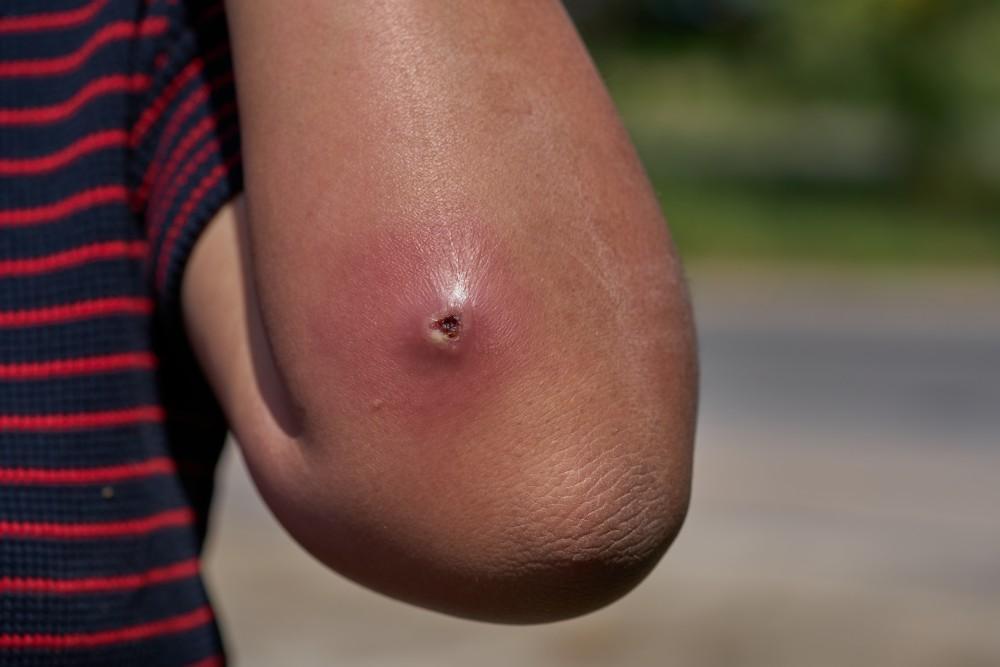
An abscess is a localized collection of pus within a cavity formed by the body’s immune system to wall off and combat an infection. Pus is a thick, yellowish fluid consisting of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. Abscesses can form anywhere in the body, including the skin, internal organs, and even the brain.
Causes of Abscesses
- Bacterial Infection: The most common cause of abscesses is a bacterial infection. When bacteria invade the body, the immune system responds by sending white blood cells to the infected area to fight off the invaders. This immune response can lead to the formation of an abscess as the body tries to contain the infection.
- Blocked Glands or Hair Follicles: Abscesses can also occur when glands or hair follicles become blocked. This can happen in conditions like hidradenitis suppurativa or folliculitis, leading to the formation of painful abscesses.
- Dental Infections: Dental abscesses are often the result of tooth decay, gum disease, or dental procedures. These can cause severe pain and swelling around the affected tooth or gums.
Symptoms of Abscesses
The symptoms of an abscess can vary depending on its location and severity. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Abscesses are typically painful, and the pain may be throbbing or constant.
- Swelling: The affected area is usually swollen, red, and warm to the touch.
- Pus Drainage: In some cases, an abscess may spontaneously rupture, causing pus to drain out. This can provide temporary relief but requires proper medical attention.
- Fever: Systemic symptoms like fever and chills may develop if the infection spreads.
- Skin Changes: If the abscess is on the skin, it may cause the skin to become shiny and stretched.
Treatment Options
- Antibiotics: In cases where the abscess is small and the infection is not severe, a course of antibiotics may be prescribed to help the body fight off the infection. However, antibiotics alone may not be sufficient to treat larger abscesses.
- Incision and Drainage: For larger or deeply situated abscesses, a healthcare provider may need to make an incision to drain the pus. This is usually done under local anesthesia to minimize pain.
- Surgical Removal: In some cases, especially with recurring or chronic abscesses, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected tissue or cyst.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may be recommended to manage pain and discomfort associated with abscesses.
Preventing Abscesses
Preventing abscesses largely depends on maintaining good hygiene and avoiding activities that can introduce bacteria into the body. Here are some preventive measures:
- Practice good hand hygiene to reduce the risk of infection.
- Keep wounds clean and properly dressed.
- Maintain oral hygiene to prevent dental abscesses.
- Manage chronic skin conditions like acne, hidradenitis suppurativa, and folliculitis under medical supervision.
Conclusion
Abscesses can be painful and, if left untreated, potentially dangerous. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention is essential for effective treatment and prevention of complications. While antibiotics and drainage can help manage abscesses, maintaining good hygiene and practicing preventive measures are key steps in reducing the risk of these uncomfortable infections. Always consult a primary care physician for proper diagnosis and treatment of abscesses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an abscess?
- An abscess is a localized collection of pus within a cavity formed by the body’s immune response to fight off an infection.
2. What causes abscesses?
- Abscesses are primarily caused by bacterial infections. They can also result from blocked glands or hair follicles, dental issues, or other factors that introduce bacteria into the body.
3. Where can abscesses occur in the body?
- Abscesses can occur anywhere in the body, including the skin, internal organs, and even the brain.
4. What are the common symptoms of an abscess?
- Typical symptoms include pain, swelling, redness, warmth at the affected area, pus drainage, fever, and in skin abscesses, the skin may appear shiny and stretched.
5. Are there different types of abscess?
- Yes, abscess can be categorized into various types, such as skin abscess, dental abscess, and internal abscess based on their location.
6. How are abscess treated?
- Treatment depends on the size and location of the abscess. It may include antibiotics, incision and drainage, surgical removal, and pain management medications.
7. Can abscesses go away on their own?
- Smaller abscess may rupture and drain spontaneously, but it’s important to seek medical attention to prevent complications or recurrence.
8. What should I do if I suspect I have an abscess?
- If you suspect you have an abscess, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
9. How can abscess be prevented?
- Maintaining good hygiene, practicing proper wound care, and managing chronic skin conditions can help reduce the risk of abscess. Dental hygiene is crucial for preventing dental abscess.
10. Are abscess dangerous?
- Abscess can be dangerous if left untreated or if the infection spreads. Seeking timely medical care is essential to prevent complications.