Business
Anatomy: Unveiling the Wonders of the Human and Body
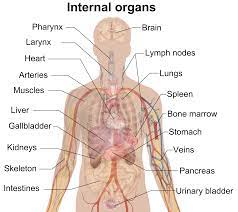
Anatomy, often referred to as the foundation of medical and biological sciences, is the study of the structure and organization of living organisms. In particular, human anatomy focuses on understanding the complexities of the human body. This field of science is crucial for medical professionals, biologists, and anyone curious about the inner workings of the human form. In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of anatomy, shedding light on the intricacies of the human body’s structure and functions.
The Core Concepts of Anatomy
Anatomy is a multifaceted discipline, and it can be divided into several core concepts:
- Gross Anatomy: This branch deals with the examination of structures that can be observed with the naked eye. It includes the study of organs, tissues, and systems.
- Microscopic Anatomy: Also known as histology, this area involves the study of tissues and cells under a microscope, exploring their cellular structure and organization.
- Developmental Anatomy: This aspect focuses on the changes in structure and form as an organism grows from a single cell to a complex multicellular organism.
- Comparative Anatomy: Comparative anatomy involves the comparison of anatomical structures among different species to understand evolutionary relationships and adaptations.
- Functional Anatomy: This branch explores the relationship between structure and function within the human body. It investigates how anatomical features enable various bodily functions.
- Clinical Anatomy: Clinical anatomy is of paramount importance in the medical field. It concentrates on the application of anatomical knowledge to clinical practice, such as surgery and medical diagnostics.
Systems of the Human Body
Anatomy dissects the human body into several systems, each with its distinct functions. Some of the major systems include:
- Skeletal System: The skeletal system comprises bones and joints, providing support, protection, and structure to the body.
- Muscular System: This system consists of muscles and tendons that allow movement and provide the force required for bodily functions.
- Circulatory System: The circulatory system includes the heart and blood vessels, facilitating the circulation of blood and the transportation of nutrients and oxygen to cells.
- Nervous System: The nervous system is responsible for sending and receiving signals, controlling bodily functions, and regulating behavior.
- Respiratory System: This system encompasses the lungs and airways, enabling the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment.
- Digestive System: The digestive system processes food and absorbs nutrients, consisting of the stomach, intestines, and associated organs.
- Reproductive System: The reproductive system differs between males and females and is responsible for reproduction and the production of sex hormones.
- Urinary System: The urinary system, including the kidneys and bladder, regulates fluid balance and filters waste products from the bloodstream.
- Endocrine System: The endocrine system manages hormonal regulation, using glands to secrete hormones that influence various bodily functions.
- Integumentary System: The skin, hair, and nails form the integumentary system, providing protection and sensory functions.
Importance of Anatomy in Medicine
Anatomy is the foundation of medical practice, underpinning the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions. Understanding the human body’s structure is essential for physicians, surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. Here’s how anatomy plays a pivotal role in medicine:
- Medical Education: Medical students must undergo rigorous anatomy courses to comprehend the intricacies of the human body. These courses often involve dissection of cadavers to gain a hands-on understanding of anatomical structures.
- Clinical Diagnosis: Physicians use their knowledge of anatomy to diagnose diseases and conditions. They identify symptoms, localize problems, and plan treatments based on an accurate understanding of the body’s structure.
- Surgical Procedures: Surgeons rely on precise anatomical knowledge when performing surgical procedures. A thorough understanding of the location and function of organs and tissues is essential for successful surgeries.
- Medical Imaging: Modern medical imaging technologies, such as MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound, allow healthcare professionals to visualize internal structures and detect abnormalities.
- Patient Communication: Physicians use their knowledge of anatomy to explain medical conditions and treatment options to patients, ensuring that individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare.
The Role of Anatomy in Research
Anatomy is not limited to the practice of medicine. It also plays a vital role in scientific research. Researchers use anatomical knowledge to study diseases, conduct experiments, and develop new medical technologies. Some areas of research where anatomy is fundamental include:
- Comparative Anatomy: Comparative anatomists study the anatomy of different species to understand evolutionary relationships and adaptations.
- Biomechanics: Biomechanical researchers analyze the mechanical aspects of anatomical structures, helping design prosthetics, orthopedic devices, and improving sports performance.
- Embryology: Embryologists study the development of organisms from a single cell to a complex multicellular organism, providing insights into birth defects and genetic conditions.
- Forensic Science: Forensic anatomists use anatomical knowledge to examine human remains, aiding in the identification of individuals and determination of the cause of death.
- Molecular Anatomy: With advancements in genetics, molecular anatomists investigate the role of genes and proteins in anatomical structures and functions.
The Continual Advancements in Anatomy
The field of anatomy is not static; it continues to evolve with new discoveries and technologies. Advancements in medical imaging, such as 3D visualization and virtual anatomy, have enhanced the study of anatomy. These technologies enable medical students and researchers to explore anatomical structures in depth without the need for physical dissection.
Moreover, regenerative medicine and tissue engineering are fields that leverage anatomical knowledge to develop new medical treatments. Researchers are working to repair and replace damaged or lost tissues and organs through a deep understanding of anatomy.
Conclusion
Anatomy is the cornerstone of our understanding of the human body and living organisms. It provides the basis for medical practice, scientific research, and advancements in healthcare. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the human form and the intricacies of life’s structures, the field of anatomy remains a vital and dynamic discipline. It not only informs our understanding of the body but also paves the way for innovative medical treatments and scientific discoveries.


