Home
Introduction to Zeotropic and Azeotropic Mixtures
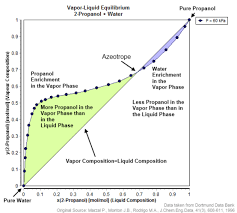
In the world of chemistry and industrial processes, mixtures are commonplace. Two specific types of mixtures, zeotropic and azeotropic, play significant roles in various applications. Understanding the differences between these two can be crucial for scientists, engineers, and chemists. In this article, we’ll delve into the dissimilarities, applications, and importance of zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures.
Zeotropic vs. Azeotropic Mixtures: Which Is Better?
The choice between zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures depends on the specific needs of the industry or process. Each has its advantages and disadvantages, and the decision should be based on the desired outcome.
Practical Examples and Use Cases
To illustrate their significance, let’s explore practical examples where zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures are employed, showcasing the real-world applications of these mixtures.
Factors Influencing Mixture Types
Several factors, including temperature, pressure, and chemical properties, influence whether a mixture will be zeotropic or azeotropic. Understanding these factors is essential for designing processes effectively.
The Role of Phase Diagrams
Phase diagrams are valuable tools for understanding the behavior of mixtures under varying conditions. They provide essential insights into how zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures behave during phase changes.
Challenges in Handling Zeotropic and Azeotropic Mixtures
While these mixtures offer unique benefits, they also present challenges in handling and separation. Overcoming these challenges is a crucial aspect of working with these mixtures effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures are two important types of mixtures in the world of chemistry and industry. Their varying compositions, boiling points, and properties make them suitable for different applications. Understanding the differences between them is essential for successful utilization.
Understanding Zeotropic Mixtures
2.1. Definition
Zeotropic mixtures are non-azeotropic mixtures in which the components have different boiling points. This means that when such a mixture is heated, the components evaporate at different rates. Zeotropic mixtures are commonly encountered in the chemical industry, where precise control over component ratios is essential.
2.2. Examples
Some well-known examples of zeotropic mixtures include the refrigerants used in air conditioning systems. These mixtures ensure efficient cooling by allowing the separate evaporation of components at different temperatures.
2.3. Properties
Zeotropic mixtures exhibit variable compositions and boiling points, making them useful for a wide range of applications. Their properties make them ideal for industries requiring controlled thermal processes.
Azeotropic Mixtures: What Are They?
3.1. Definition
Azeotropic mixtures, in contrast, are special types of mixtures where the components have the same boiling point. When an azeotropic mixture is heated, it evaporates at a constant composition, making separation processes challenging.
3.2. Examples
A classic example of an azeotropic mixture is the mixture of ethanol and water, often encountered in distillation processes. Despite varying ratios, this mixture boils at a constant temperature, making complete separation impossible.
3.3. Properties
Azeotropic mixtures are known for their consistent composition during vaporization, a property that can be both advantageous and problematic, depending on the application.
Key Differences Between Zeotropic and Azeotropic Mixtures
4.1. Composition
The primary difference lies in the composition. Zeotropic mixtures have varying component ratios, whereas azeotropic mixtures maintain constant compositions.
4.2. Boiling Point
Zeotropic mixtures have components with different boiling points, while azeotropic mixtures have components with the same boiling points.
4.3. Separation
Zeotropic mixtures can be separated into their individual components by controlling temperature and pressure, whereas azeotropic mixtures are notoriously challenging to separate.
4.4. Industrial Applications
Zeotropic mixtures are commonly used in applications requiring controlled evaporation, while azeotropic mixtures can be found in processes where maintaining a constant composition is necessary.
Importance in Chemistry and Industry
Both zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures are vital in various industries. Their unique properties are leveraged in the pharmaceutical, chemical, and food industries, among others. These mixtures enable precise control and optimization of processes.
Zeotropic vs. Azeotropic Mixtures: Which Is Better?
The choice between zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures depends on the specific needs of the industry or process. Each has its advantages and disadvantages, and the decision should be based on the desired outcome.
Practical Examples and Use Cases
To illustrate their significance, let’s explore practical examples where zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures are employed, showcasing the real-world applications of these mixtures.
Factors Influencing Mixture Types
Several factors, including temperature, pressure, and chemical properties, influence whether a mixture will be zeotropic or azeotropic. Understanding these factors is essential for designing processes effectively.
The Role of Phase Diagrams
Phase diagrams are valuable tools for understanding the behavior of mixtures under varying conditions. They provide essential insights into how zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures behave during phase changes.
Challenges in Handling Zeotropic and Azeotropic Mixtures
While these mixtures offer unique benefits, they also present challenges in handling and separation. Overcoming these challenges is a crucial aspect of working with these mixtures effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures are two important types of mixtures in the world of chemistry and industry. Their varying compositions, boiling points, and properties make them suitable for different applications. Understanding the differences between them is essential for successful utilization.
FAQs
- What are zeotropic mixtures used for? Zeotropic mixtures are used in industries where precise control over component ratios and evaporation rates is necessary, such as in the production of refrigerants.
- Can azeotropic mixtures be separated? Azeotropic mixtures are notoriously challenging to separate completely due to their constant composition during vaporization.
- How do phase diagrams help in understanding mixtures? Phase diagrams provide insights into how zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures behave under varying temperature and pressure conditions, aiding in process design.
- Are zeotropic or azeotropic mixtures better for distillation processes? The choice depends on the specific requirements of the process. Zeotropic mixtures allow controlled separation, while azeotropic mixtures maintain constant composition.
- What industries benefit most from zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures? Industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing benefit from the unique properties of these mixtures for precise control and optimization of processes.
Get Access Now: https://bit.ly/J_Umma
This comprehensive article should provide readers with a thorough understanding of zeotropic and azeotropic mixtures and their importance in various industries.


