Business
The Core Concepts of Biology
What is Biology?
Biology is the study of living organisms and their interactions with the environment. It explores the structure, function, growth, evolution, and distribution of life on Earth.
The Scientific Method
Biology relies on the scientific method to form hypotheses, conduct experiments, and draw conclusions, ensuring that the findings are accurate and reliable.
Cell Theory
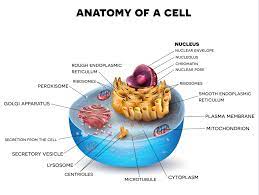
At the heart of biology lies the cell, the fundamental unit of life. Cell theory states that all living things are composed of cells and that cells are the basic structural and functional units of life.
The Diversity of Life
Taxonomy and Classification
Taxonomy categorizes and classifies organisms based on shared characteristics. It helps us understand the relationships between different species.
Domains and Kingdoms
The classification of life includes three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. These domains further branch into kingdoms, which categorize organisms more specifically.
Biodiversity
The Earth is teeming with diverse life forms. Biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem stability and human well-being.
Genetics and Inheritance
DNA and Genetic Information
The discovery of DNA as the genetic material revolutionized biology. It holds the instructions for an organism’s development and function.
Mendelian Genetics
Gregor Mendel’s experiments with pea plants laid the foundation for our understanding of inheritance. His principles of dominant and recessive traits are fundamental.
Genetic Variation
Genetic diversity is essential for species’ adaptability and survival in a changing environment.
Evolution and Natural Selection
Charles Darwin’s Theory
Darwin’s theory of evolution through natural selection explains how species change over time in response to environmental pressures.
Evidence for Evolution
Fossils, comparative anatomy, and molecular biology provide compelling evidence for the evolutionary history of life on Earth.
Adaptation and Survival
Adaptations enable organisms to thrive in their environments, showcasing the power of natural selection.
Ecology and Ecosystems
Interactions in Ecosystems
Ecosystems are complex webs of interactions between organisms and their environments, highlighting the delicate balance of nature.
Energy Flow
The flow of energy through ecosystems sustains life and defines the trophic levels within food chains.
Conservation Biology
Conservation biology aims to protect and restore biodiversity, addressing critical issues like habitat destruction and climate change.
Human Biology
Anatomy and Physiology
Understanding the structure and function of the human body is essential for the practice of medicine and healthcare.
Health and Disease
The study of human health and diseases equips us with knowledge to prevent and treat medical conditions.
Genetics in Medicine
Genetics plays a vital role in identifying and treating genetic diseases and disorders.
Microbiology
Bacteria and Archaea
Microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea, are essential for various biotechnological and ecological processes.
Viruses
Viruses, although not considered living organisms, have a significant impact on health and the environment.
Microorganisms and Health
The study of microorganisms is critical for understanding infectious diseases and biotechnology.
Botany: The Study of Plants
Plant Anatomy and Physiology
Plants are the primary producers in ecosystems, and their structure and function are integral to life on Earth.
Plant Diversity
The plant kingdom is incredibly diverse, with various adaptations and life strategies.
Plant Adaptations
Plants have evolved unique adaptations to thrive in various environments, from deserts to rainforests.
Zoology: The Study of Animals
Animal Classification
Zoology involves the classification of animals, from invertebrates to vertebrates, based on their characteristics.
Animal Behavior
Studying animal behavior provides insights into their evolutionary strategies, communication, and social structures.
Wildlife Conservation
Zoologists work to protect endangered species and conserve wildlife habitats to maintain the Earth’s biodiversity.
Molecular Biology
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering allows scientists to modify DNA for various applications, including medical treatments and crop improvement.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology leverages biological processes for practical applications, from producing medicines to biofuels.
DNA Sequencing
Advancements in DNA sequencing have transformed our ability to decode the genetic information of organisms.
Ecological Issues and Conservation
Climate Change
Climate change is a pressing global concern, impacting ecosystems and species worldwide.
Endangered Species
Numerous species face the threat of extinction due to habitat loss, pollution, and overexploitation.
Environmental Protection
Efforts to protect the environment are crucial for preserving the balance of life on Earth.
The Future of Biology
Emerging Technologies
The future of biology is bright, with emerging technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 and gene editing revolutionizing the field.
Advancements in Biomedicine
Biomedicine continues to advance, offering new hope for treating diseases and improving human health.
Ethical Considerations
As biology progresses, ethical questions arise regarding genetic manipulation and environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
Biology is a captivating journey into the intricate web of life on Earth. It helps us appreciate the wonders of the natural world, and its insights are crucial for addressing current
Defining Biology
Biology is the scientific study of living organisms and their interactions with the environment. It delves into the structure, function, growth, evolution, and distribution of life on Earth.
The Scientific Approach
Biology relies on the scientific method to form hypotheses, conduct experiments, and draw sound conclusions. This rigorous process ensures the accuracy and reliability of biological findings.
The Significance of Cells
At the heart of biology lies the cell, the fundamental unit of life. The cell theory posits that all living entities are composed of cells and that cells are the basic structural and functional components of life.
The Kaleidoscope of Life
Taxonomy and Categorization
Taxonomy is the science of categorizing and classifying organisms based on shared characteristics. It provides a framework to comprehend the relationships between different species.
The Three Domains of Life
Life on Earth is categorized into three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya, which, in turn, branch into kingdoms, offering a more refined classification of organisms.
Celebrating Biodiversity
Our planet boasts a rich tapestry of life. Biodiversity is crucial for the stability of ecosystems and the well-being of humanity.
Genetics: The Blueprint of Life
DNA’s Enigmatic Code
The discovery of DNA as the genetic material marked a turning point in biology. It contains the instructions for an organism’s development and function.
Embracing Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity is essential for the adaptability and survival of species in an ever-changing environment.
Evolution: Nature’s Masterpiece
Darwin’s Vision
Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution through natural selection explains how species transform over time in response to environmental pressures.
The Compelling Evidence for Evolution
Fossils, comparative anatomy, and molecular biology offer convincing evidence of the evolutionary history of life on our planet.
Adaptation and Survival of the Fittest
Adaptations enable organisms to thrive in their environments, showcasing the power of natural selection.
Ecology: The Harmonious Web
Ecosystem Dynamics
Ecosystems are intricate networks of interactions between organisms and their surroundings, highlighting the delicate balance of nature.
The Flow of Energy
The flow of energy through ecosystems sustains life and defines the trophic levels within food chains.
Preserving Biodiversity
Conservation biology aims to safeguard and restore biodiversity, addressing critical issues such as habitat destruction and climate change.
Human Biology: Our Inner Workings
The Complexities of Anatomy and Physiology
Understanding the structure and function of the human body is fundamental to the fields of medicine and healthcare.
Navigating Health and Disease
The study of human health and diseases equips us with the knowledge needed to prevent and treat medical conditions.
Genetics in Medical Science
Genetics plays a pivotal role in identifying and treating genetic diseases and disorders, offering insights into personalized medicine and healthcare.
Microbiology: The Hidden Microcosm
Exploring Bacteria and Archaea
Microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea, are integral to various biotechnological and ecological processes.
The Enigmatic World of Viruses
Viruses, although not classified as living organisms, exert significant impacts on health and the environment.
Microorganisms in Health and Beyond
The study of microorganisms is critical for understanding infectious diseases, biotechnology, and their role in diverse ecosystems.
Botany: The Study of Plant Life
The Intricacies of Plant Anatomy and Physiology
Plants are the primary producers in ecosystems, and their structure and function are integral to life on Earth.
The Diverse Kingdom of Plants
The plant kingdom is incredibly diverse, showcasing various adaptations and life strategies to thrive in diverse environments.
Plant Survival Strategies
Plants have evolved unique adaptations to flourish in diverse habitats, from arid deserts to lush rainforests.
Zoology: The Animal Kingdom Unveiled
The Classification of Animals
Zoology involves the classification of animals, ranging from invertebrates to vertebrates, based on their distinct characteristics.
Decoding Animal Behavior
Studying animal behavior provides insights into their evolutionary strategies, communication methods, and social structures.


