Entertainment
Weather vs. Whether: Demystifying the Difference with
In the vast and often confusing landscape of the English language, homophones are a common source of errors and misunderstandings. Two such words that frequently cause confusion are “weather” and “whether.” Though they sound identical when spoken, these words have distinct meanings and are used in different contexts. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the difference between “weather” and “whether” and provide numerous examples to illustrate their proper usage.
Whether: Expressing a Choice or Condition
“Whether,” on the other hand, is a conjunction used to express a condition with two possible outcomes or to introduce a choice between alternatives. Here are the primary definitions and examples:
- Expressing a Choice: “Whether” is commonly used to introduce a clause where a choice is being considered or expressed. Example: I can’t decide whether to go to the beach or stay at home.
- Introducing Alternatives: It can be used to present two or more alternatives or possibilities. Example: The question is whether we should invest in stocks, bonds, or real estate.
- Condition: In some cases, “whether” is used to introduce a conditional clause. Example: I’ll go for a walk, whether or not it rains.
Examples of Correct Usage
To clarify the distinction between “weather” and “whether,” let’s explore a range of examples demonstrating their correct usage:
Weather Examples:
- The weather in the mountains can change rapidly, so hikers should be prepared for sudden storms.
- The weather report indicates that the temperature will drop below freezing tonight.
- The severe weather conditions forced the cancellation of the outdoor event.
- She always checks the weather forecast before planning a picnic.
- Extreme weather events, like hurricanes, can cause significant damage.
Whether Examples:
- I can’t decide whether I should order pizza or pasta for dinner.
- They are uncertain whether the meeting will be held in person or virtually.
- The question is whether he will accept the job offer or continue searching for a better opportunity.
- She asked whether he would attend the party or stay home.
- We need to determine whether the project is feasible within our budget.
Conclusion
In conclusion, “weather” and “whether” may sound identical in speech, but they serve entirely different purposes in the English language. “Weather” relates to atmospheric conditions and can be used as both a noun and a verb. “Whether” is a conjunction used to introduce choices, conditions, or alternatives in sentences. Distinguishing between these two words is vital for clear and effective communication in written and spoken English.
By mastering the appropriate use of “weather” and “whether,” you can enhance your language skills and avoid common grammatical errors. So, whether you’re discussing the weather or considering whether to use “whether” correctly, these distinctions will be invaluable in your language journey.
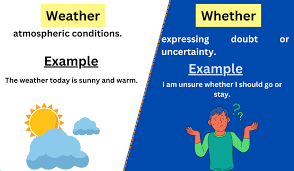
Weather: The Atmospheric Conditions
The word “weather” is primarily a noun, although it can also be used as a verb in some contexts. It pertains to the atmospheric conditions at a particular place and time. Here are the key definitions and examples:
- Meteorological Conditions: “Weather” refers to the state of the atmosphere, including elements like temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind, and atmospheric pressure. Example: The weather forecast predicts rain and thunderstorms tomorrow.
- Climate and Seasons: It can also refer to the long-term atmospheric conditions in a particular region, as well as the characteristic conditions during specific seasons. Example: The weather in this region is known for its mild winters.
- Verb Usage: As a verb, “weather” means to withstand or endure adverse conditions. Example: The old lighthouse has weathered countless storms over the years.
Whether: Expressing a Choice or Condition
“Whether,” on the other hand, is a conjunction used to express a condition with two possible outcomes or to introduce a choice between alternatives. Here are the primary definitions and examples:
- Expressing a Choice: “Whether” is commonly used to introduce a clause where a choice is being considered or expressed. Example: I can’t decide whether to go to the beach or stay at home.
- Introducing Alternatives: It can be used to present two or more alternatives or possibilities. Example: The question is whether we should invest in stocks, bonds, or real estate.
- Condition: In some cases, “whether” is used to introduce a conditional clause. Example: I’ll go for a walk, whether or not it rains.
Examples of Correct Usage
To clarify the distinction between “weather” and “whether,” let’s explore a range of examples demonstrating their correct usage:
Weather Examples:
- The weather in the mountains can change rapidly, so hikers should be prepared for sudden storms.
- The weather report indicates that the temperature will drop below freezing tonight.
- The severe weather conditions forced the cancellation of the outdoor event.
- She always checks the weather forecast before planning a picnic.
- Extreme weather events, like hurricanes, can cause significant damage.
Whether Examples:
- I can’t decide whether I should order pizza or pasta for dinner.
- They are uncertain whether the meeting will be held in person or virtually.
- The question is whether he will accept the job offer or continue searching for a better opportunity.
- She asked whether he would attend the party or stay home.
- We need to determine whether the project is feasible within our budget.
Conclusion
In conclusion, “weather” and “whether” may sound identical in speech, but they serve entirely different purposes in the English language. “Weather” relates to atmospheric conditions and can be used as both a noun and a verb. “Whether” is a conjunction used to introduce choices, conditions, or alternatives in sentences. Distinguishing between these two words is vital for clear and effective communication in written and spoken English.
By mastering the appropriate use of “weather” and “whether,” you can enhance your language skills and avoid common grammatical errors. So, whether you’re discussing the weather or considering whether to use “whether” correctly, these distinctions will be invaluable in your language journey.