Home
Zeotropic Mixtures: Types and Wide-Ranging Applications
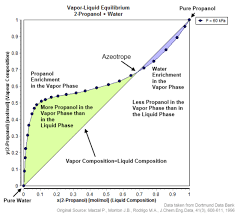
Zeotropic mixtures are a fascinating aspect of thermodynamics and chemical engineering. Their non-constant boiling behavior and changing composition during phase transitions make them invaluable in various industrial applications. In this article, we will explore the types of zeotropic mixtures and their diverse range of real-world applications.
Environmental Protection
The use of zeotropic mixtures in refrigeration and air conditioning systems contributes to environmental protection by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and ozone depletion. These mixtures align with global efforts to address climate change.
The Future of Zeotropic Mixtures
As technology advances and environmental concerns become more pressing, zeotropic mixtures are likely to play an increasingly vital role in various industries. The development of innovative distillation techniques, improved refrigeration systems, and the application of zeotropy to new fields continue to shape their role in modern engineering and sustainability.
Conclusion
Zeotropic mixtures are a remarkable aspect of thermodynamics and chemical engineering, offering unique properties that challenge conventional distillation techniques. Despite their complexities, zeotropic mixtures find applications in various industries, from refrigeration and air conditioning to petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals.
As the world shifts toward more sustainable and eco-friendly practices, zeotropic mixtures will continue to be at the forefront of technological advancements and environmental protection, making them a crucial element of the modern industrial landscape.
Understanding Zeotropic Mixtures
Before we delve into the types and applications, let’s recap the fundamentals of zeotropic mixtures. Zeotropy is a property of mixtures where the components have different volatility, which leads to varying boiling points. In a zeotropic mixture, as it is heated or cooled, the composition of the vapor phase differs from that of the liquid phase.
Key Characteristics of Zeotropic Mixtures:
- Changing Composition: Zeotropic mixtures exhibit varying compositions in the vapor and liquid phases during phase transitions, particularly during distillation.
- Complex Separation: The changing composition poses challenges in the separation of components, often requiring sophisticated distillation techniques.
- Practical Versatility: Zeotropic mixtures find applications in a wide range of industries due to their unique thermodynamic properties.
Types of Zeotropic Mixtures
Zeotropic mixtures come in various types, primarily classified based on the nature of the components and their behavior during phase transitions. Let’s explore some common types:
Type I Zeotropes
Type I zeotropes are mixtures of components that have positive deviations from Raoult’s law. In these mixtures, the components have varying affinities for each other, leading to a non-constant boiling point and changing compositions during the phase transition.
Example: One well-known Type I zeotrope is the mixture of ethanol and water, used in the production of alcoholic beverages. The composition changes during distillation, affecting the product’s flavor and alcohol content.
Type II Zeotropes
Type II zeotropes are mixtures where the components have negative deviations from Raoult’s law. These mixtures exhibit a changing composition during distillation, but unlike Type I zeotropes, the composition shift occurs in the opposite direction.
Example: A Type II zeotrope is the mixture of acetone and chloroform. As it is distilled, the chloroform concentration in the vapor phase increases, while the acetone concentration in the liquid phase rises.
Type III Zeotropes
Type III zeotropes are characterized by multiple azeotropes in the phase diagram. They have a complex behavior, often displaying multiple temperature plateaus during distillation.
Example: The mixture of ethanol, water, and ethyl acetate is a Type III zeotrope. It exhibits multiple azeotropes and complex phase behavior during distillation.
Applications of Zeotropic Mixtures
Zeotropic mixtures find diverse applications across various industries due to their unique thermodynamic properties. Here are some notable applications:
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
Zeotropic refrigerants are used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems. While their changing compositions pose challenges, they offer better environmental properties compared to older refrigerants like CFCs and HCFCs. Zeotropic mixtures are employed in:
- Residential Air Conditioning: Systems that use zeotropic refrigerants are more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient.
- Commercial Refrigeration: Supermarkets and restaurants use zeotropic mixtures in their refrigeration systems to reduce environmental impact.
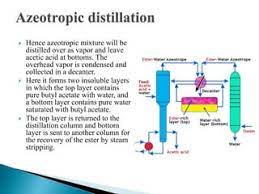
Distillation Processes
In chemical engineering, zeotropic mixtures are crucial in distillation processes for the separation of components with varying boiling points. Distillation is employed in:
- Petrochemical Industry: Separating crude oil into various hydrocarbon products such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
- Pharmaceuticals: Purifying and separating different chemical compounds in drug manufacturing.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Separating and purifying substances in the production of alcoholic beverages, including whiskey and vodka.
Solvent Recovery
Zeotropic mixtures are used in solvent recovery processes, where they allow for the efficient separation and recycling of solvents used in various industrial processes. This reduces waste and environmental impact.
Environmental Protection
The use of zeotropic mixtures in refrigeration and air conditioning systems contributes to environmental protection by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and ozone depletion. These mixtures align with global efforts to address climate change.
The Future of Zeotropic Mixtures
As technology advances and environmental concerns become more pressing, zeotropic mixtures are likely to play an increasingly vital role in various industries. The development of innovative distillation techniques, improved refrigeration systems, and the application of zeotropy to new fields continue to shape their role in modern engineering and sustainability.
Conclusion
Zeotropic mixtures are a remarkable aspect of thermodynamics and chemical engineering, offering unique properties that challenge conventional distillation techniques. Despite their complexities, zeotropic mixtures find applications in various industries, from refrigeration and air conditioning to petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals.
As the world shifts toward more sustainable and eco-friendly practices, zeotropic mixtures will continue to be at the forefront of technological advancements and environmental protection, making them a crucial element of the modern industrial landscape.